Multiple Intelligences
Take the Multiple Intelligences Test to see your strongest abilities.
Howard Gardner, a graduate of Harvard University and a developmental psychologist, developed the theory of Multiple Intelligences in 1986. Gardner believes that intelligence, the way it has traditionally been understood (logically, as with I.Q. tests), does not explain the wide variety of human abilities. The theory of Multiple Intelligences suggests that we excel with different types of intelligence.
In addition to being logical and Number Smart, a person might also be Word Smart, People Smart or Picture Smart. Gardner has identified the following intelligences: Verbal/Linguistic, Logical/Mathematical, Visual/Spatial, Bodily/Kinesthetic, Musical, Intrapersonal, Interpersonal and Naturalist.
About the Intelligences

Verbal/Linguistic Intelligence
People with Linguistic intelligence are naturally good with writing or speaking and memorization.
Logical/Mathematical Intelligence
People with Logical intelligence are driven by logic and reasoning.
Visual/Spatial Intelligence
People with Visual intelligence are good at remembering images and are aware of surroundings.
Bodily/Kinesthetic Intelligence
People with Kinesthetic intelligence love movement, have good motor skills and are aware of their bodies.
Musical Intelligence
People with musical intelligence are musically gifted and have a “good ear” for rhythm and composition.
Intrapersonal Intelligence
People with intrapersonal intelligence are adept at looking inward.
Interpersonal Intelligence
People with Interpersonal intelligence are good with people. They thrive at and enjoy social interactions.
Naturalist Intelligence
People with Naturalist intelligence have a sensitivity to and appreciation for nature. They can “see” how nature works.
Learning Styles
Take the Learning Styles Test to see what your strongest learning style is.
The theory of varying learning styles that suggests people learn better using different methods of learning. We perceive information using our senses. The three most practical senses in learning environments are sight, hearing and touch. The VAK model categorizes these sensory methods of learning as Visual (V), Auditory (A) and Kinesthetic (K) learning styles.
While most people have a dominant learning style, nobody has just one learning style. Everyone uses each of the learning styles to some degree. Some are stronger in one style while others have even strength in all styles. The reality is that we all have a custom “learning style” that is, in varying degrees, a combination of Visual, Auditory and Kinesthetic learning.
It is useful to know the strength of your learning styles as they relate to each other. This allows you to focus on maximizing your learning potential. Recognizing your strengths also helps you to seek learning opportunities that cater to your combination of learning style strengths. In recent years, many educators have started using knowledge of learning styles (and multiple intelligences) to improve teaching methods in order to reach learners of all types.
About the Learning Styles
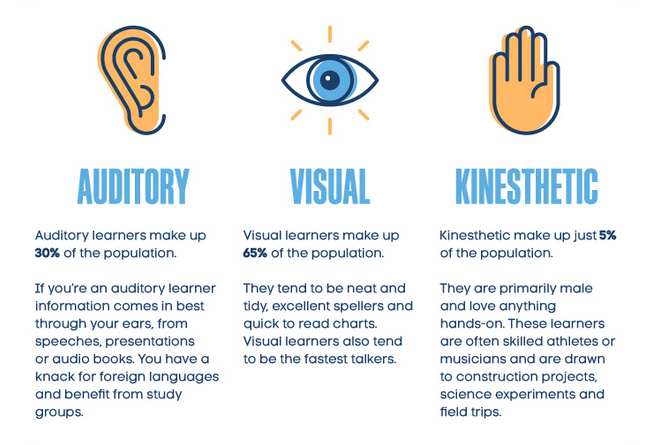
A summary of each of the VAK learning styles is provided below.
Visual Learning
The Visual learning style is learning by seeing. You learn visually whenever you gain information from sight.
Auditory Learning
Auditory style is learning by hearing. Learners with strong auditory ability are able to hear and comprehend without missing much.
Kinesthetic/Tactile Learning
Kinesthetic style is learning by doing. You learn in this manner whenever you capture new information through physical activity.